Sexually transmitted diseases (STDs) are infections that are spread through sexual contact. They can be caused by bacteria, viruses, or parasites and can affect both men and women. Understanding how these diseases are transmitted is essential for prevention and control. In this article, we will explore the various ways in which STDs can spread and provide tips on how to protect yourself.
1. Unprotected Sex
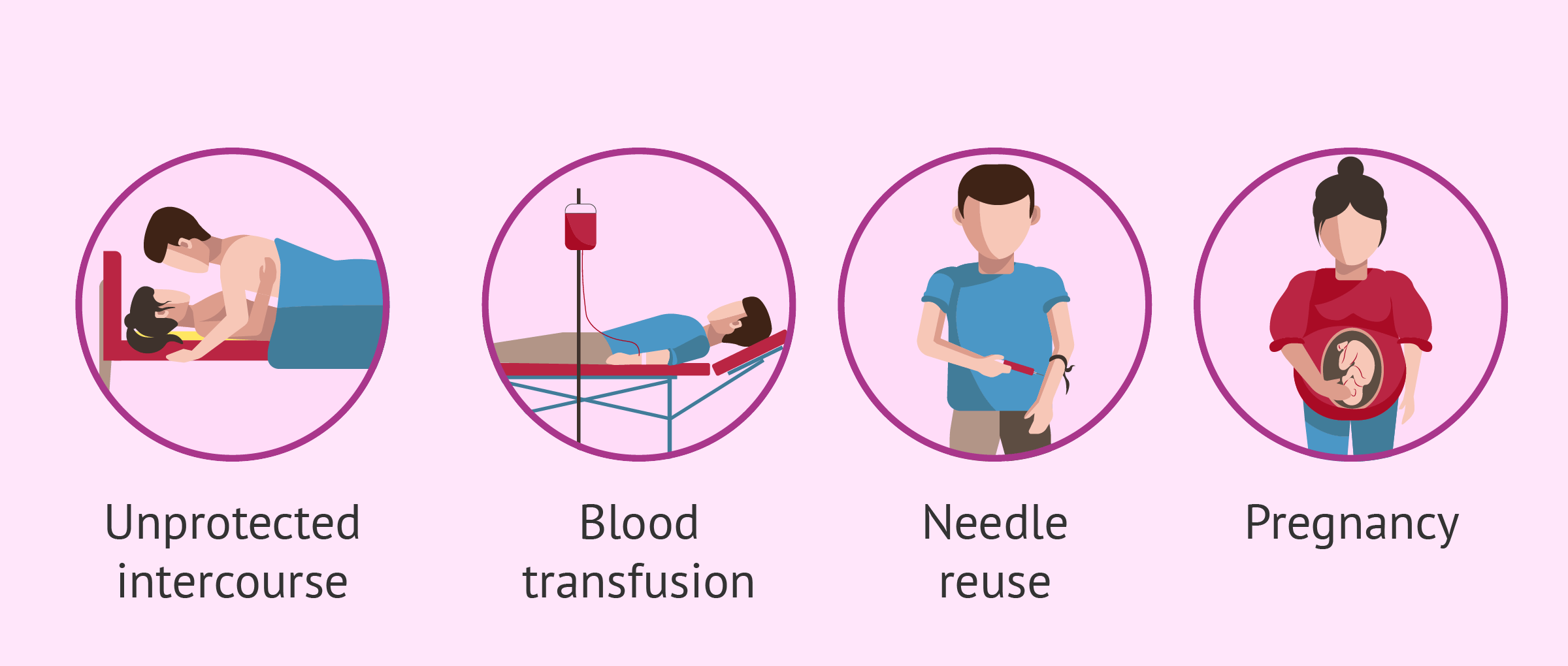
The most common way STDs spread is through unprotected sexual intercourse. This includes vaginal, anal, and oral sex. If one partner is infected with an STD, the other partner is at risk of contracting the infection. It is important to note that some STDs can be asymptomatic, meaning that infected individuals may not show any symptoms but can still transmit the disease. Therefore, using barrier methods such as condoms is crucial in reducing the risk of transmission.

Credit: www.hamiltonhealthcenter.com
2. Multiple Sexual Partners
Having multiple sexual partners increases the risk of contracting an STD. The more partners you have, the higher the chances of encountering someone who is infected. Engaging in sexual activities with different individuals without using protection significantly increases your vulnerability to STDs. It is essential to practice safe sex by using condoms consistently and getting regular screenings for STDs, especially if you have multiple partners.

Credit: medlineplus.gov
3. Sharing Needles
Some STDs, such as HIV and hepatitis, can be spread through sharing contaminated needles or other drug paraphernalia. People who inject drugs are particularly at risk of contracting these infections. Sharing needles can transfer blood-borne pathogens from one person to another, increasing the risk of STD transmission. Using clean and sterile needles and avoiding the sharing of drug equipment is vital in preventing the spread of these diseases.
4. Mother-to-Child Transmission
Pregnant women with STDs can transmit the infection to their babies during childbirth. Some STDs, such as syphilis and HIV, can be passed from mother to child through the placenta or during delivery. It is crucial for pregnant women to receive prenatal care and get tested for STDs to prevent transmission to their babies. In cases where the mother is infected, appropriate medical interventions can be implemented to reduce the risk of transmission.
5. Skin-to-Skin Contact
STDs can also be spread through direct skin-to-skin contact. This includes genital warts (caused by human papillomavirus) and herpes (caused by herpes simplex virus). Even if there are no visible sores or lesions, these infections can still be transmitted through contact with infected skin. Using barrier methods like condoms or dental dams can help reduce the risk of transmission, but it is important to note that they may not provide complete protection.
6. Oral Sex
Oral sex can also lead to the transmission of STDs. Although the risk is generally lower compared to vaginal or anal sex, it is still possible to contract infections such as herpes, syphilis, gonorrhea, and chlamydia through oral-genital contact. Using dental dams or condoms during oral sex can help reduce the risk of transmission. Regular testing for STDs is also advisable, especially if you engage in oral sex with multiple partners.
7. Lack of Vaccination
Some STDs can be prevented through vaccination. For example, the human papillomavirus (HPV) vaccine can protect against several types of HPV that can cause genital warts and certain types of cancer. The hepatitis B vaccine is also highly effective in preventing hepatitis B, a viral infection that can be transmitted sexually. It is crucial to stay up-to-date with recommended vaccinations to reduce the risk of contracting these diseases.
8. Lack of Education and Awareness
Lack of education and awareness about STDs can contribute to their spread. Many people may not be aware of the risks associated with certain sexual behaviors or the importance of using protection. Comprehensive sex education programs that provide accurate information about STDs, safe sex practices, and the importance of regular testing can help empower individuals to make informed decisions and reduce the transmission of STDs.
Conclusion
Understanding how sexually transmitted diseases spread is essential for preventing their transmission. Unprotected sex, multiple sexual partners, sharing needles, mother-to-child transmission, skin-to-skin contact, oral sex, lack of vaccination, and lack of education and awareness all contribute to the spread of STDs. By practicing safe sex, getting regular screenings, and staying informed, individuals can protect themselves and their partners from these infections. Remember, prevention is always better than cure when it comes to sexually transmitted diseases.

Ahmed bin Rashid, a seasoned travel enthusiast and visa process expert and the successful Businessman in Dubai. With an LLB from the University of Bolton in 2015, he combines his legal knowledge with his passion for exploration, offering invaluable insights into Business formation and visa processes around the globe. Follow Ahmed’s captivating journeys and expert advice to embark on your unforgettable adventures & Business.